
Introduction
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service that simplifies data analytics and reporting. Ideal for organizations handling extensive datasets, Redshift empowers users to efficiently query and analyze data using SQL. This blog will walk you through the essential aspects of Amazon Redshift, operational tasks, troubleshooting techniques, and best practices to make the most out of your data warehouse.
What is Amazon Redshift?
Amazon Redshift enables businesses to manage and analyze vast amounts of data quickly. Its architecture is designed for speed, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It supports high-performance querying and integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, making it a go-to solution for modern analytics workflows.
Key Features
- Scalability: Add or remove nodes to match performance needs.
- High Performance: Columnar storage and data compression speed up query execution.
- Integration: Connects with AWS tools like S3, Glue, and QuickSight.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go pricing with the ability to pause/resume clusters.
Operational Best Practices
- Cluster Monitoring
Regularly monitor metrics like CPU utilization, disk space usage, and query performance via CloudWatch or Redshift’s native tools. - Setting Alerts
Configure CloudWatch alarms to detect issues like resource spikes or failed queries. - Routine Maintenance
Use automated backups, regular VACUUM, and ANALYZE commands to optimize performance and ensure data consistency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Slow Query Performance
- Use Query Performance Insights to identify bottlenecks.
- Optimize table design with appropriate distribution keys and sort keys.
- Disk Space Usage
- Analyze storage with system tables like
SVV_DISKUSAGE. - Enable automatic table compression and adjust distribution styles.
- Analyze storage with system tables like
- Connectivity Problems
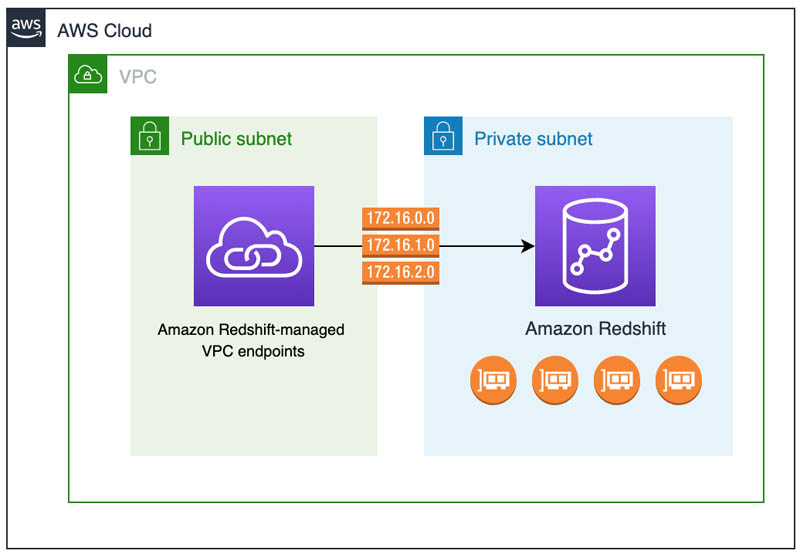
- Verify security group configurations and endpoint settings.
- Use AWS Health Dashboard to rule out regional issues.
4.High Query Concurrency
- Adjust Workload Management (WLM) settings to balance query loads.
- Implement query prioritization and monitor execution times.
Advanced Configurations
- Concurrency Scaling
Redshift automatically adds transient clusters during peak query loads, ensuring consistent performance. - Disaster Recovery
- Implement cross-region replication for high availability.
- Test failover scenarios periodically to validate recovery processes.
- Security and Compliance
- Enable encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Use IAM roles for granular access control.
Amazon Redshift is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to optimize data storage and analytics. By following the operational guidelines and troubleshooting steps outlined above, you can ensure smooth operations and leverage Redshift to its full potential. Whether managing a large data warehouse or scaling resources dynamically, Redshift has you covered.
you might be like How to Copy AWS S3 Data to Redshift Using the COPY Command.



Pingback: AWS re:Invent 2024: Data and Analytics Highlights - WCBlog