The cloud has become a cornerstone of modern technology, enabling businesses to operate efficiently, reduce costs, and scale seamlessly. This blog explores the cloud’s benefits, compares it with on-premise systems, and delves into the various cloud deployment models.

Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a range of advantages over traditional on-premise setups, transforming the way businesses manage their IT infrastructure.
1. Scalability
Cloud systems allow for easy scaling up or down based on demand. Businesses can adapt to fluctuating workloads without over-investing in hardware or infrastructure, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
2. Cost-Effectiveness (CapEx vs. OpEx)
On-premise systems require significant upfront capital expenditure (CapEx) for hardware and infrastructure. Cloud solutions, however, operate on a pay-as-you-go model, converting expenses into operational expenditure (OpEx). This reduces financial strain, particularly for startups and small businesses.
3. Agility
Setting up an on-premise system can take months, involving procurement, installation, and configuration. In contrast, cloud systems can be deployed within minutes, offering unparalleled agility. With just a click, organizations can scale their operations globally.
4. Geo-Distribution
Cloud providers host servers worldwide, minimizing latency by routing user requests to the nearest server. For instance, a user in India requesting a service won’t experience delays if servers are strategically placed in the region.
5. Disaster Recovery
With data and systems distributed globally, cloud infrastructure ensures business continuity even if a system fails in one location. Backup nodes automatically take over, maintaining seamless operations.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
Cloud computing eliminates the need for expensive, upfront investments. Organizations only pay for what they use, enabling better budgeting and cost management.
Cloud Deployment Models
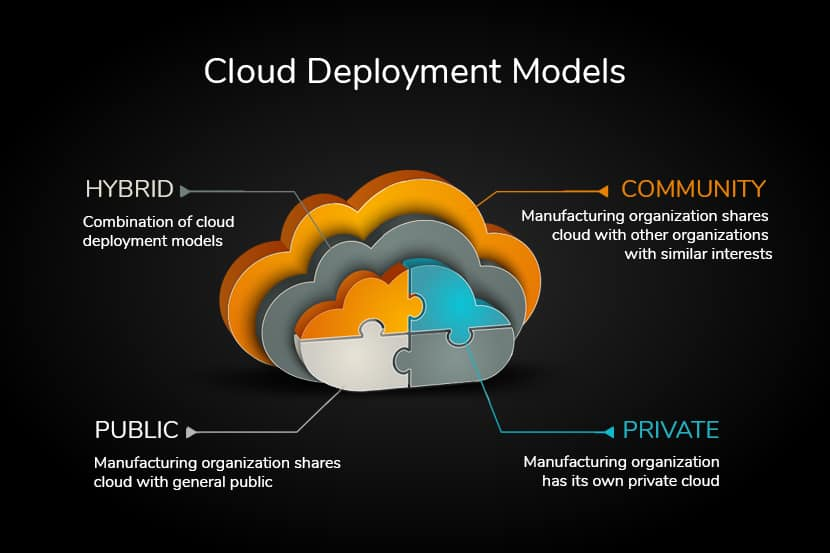
Cloud services are offered in different configurations to suit various business needs:
1. Public Cloud
Public clouds, like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), are ideal for non-sensitive data. These are cost-effective, multi-tenant environments where resources are shared among multiple users.
2. Private Cloud
Private clouds cater to organizations dealing with sensitive or confidential data, such as banks. These environments are dedicated to a single organization, offering enhanced security and control. Essentially, private clouds provide on-premise benefits with cloud flexibility.
3. Hybrid Cloud
Combining public and private clouds, hybrid cloud setups enable businesses to manage both generic and confidential data. For instance, sensitive customer information can reside in a private cloud, while public data processing can utilize the public cloud.
4. Community Cloud
A community cloud is a shared cloud infrastructure designed for a specific group of organizations with similar requirements, such as compliance or industry standards. For example, multiple hospitals might use a community cloud to securely share patient data and comply with healthcare regulations. This model provides a balance between privacy, cost-sharing, and tailored solutions for the community.
On-Premise vs. Private Cloud
While both on-premise systems and private clouds provide control over infrastructure, there are key differences:
- On-Premise: Requires setup from scratch, including procuring hardware, maintaining systems, and managing updates.
- Private Cloud: Offers the benefits of cloud management while being exclusive to a single organization. It provides a controlled environment without the need for extensive physical infrastructure.